March 20, 2024
Author : Anmol Agarwal
5 Mins Read
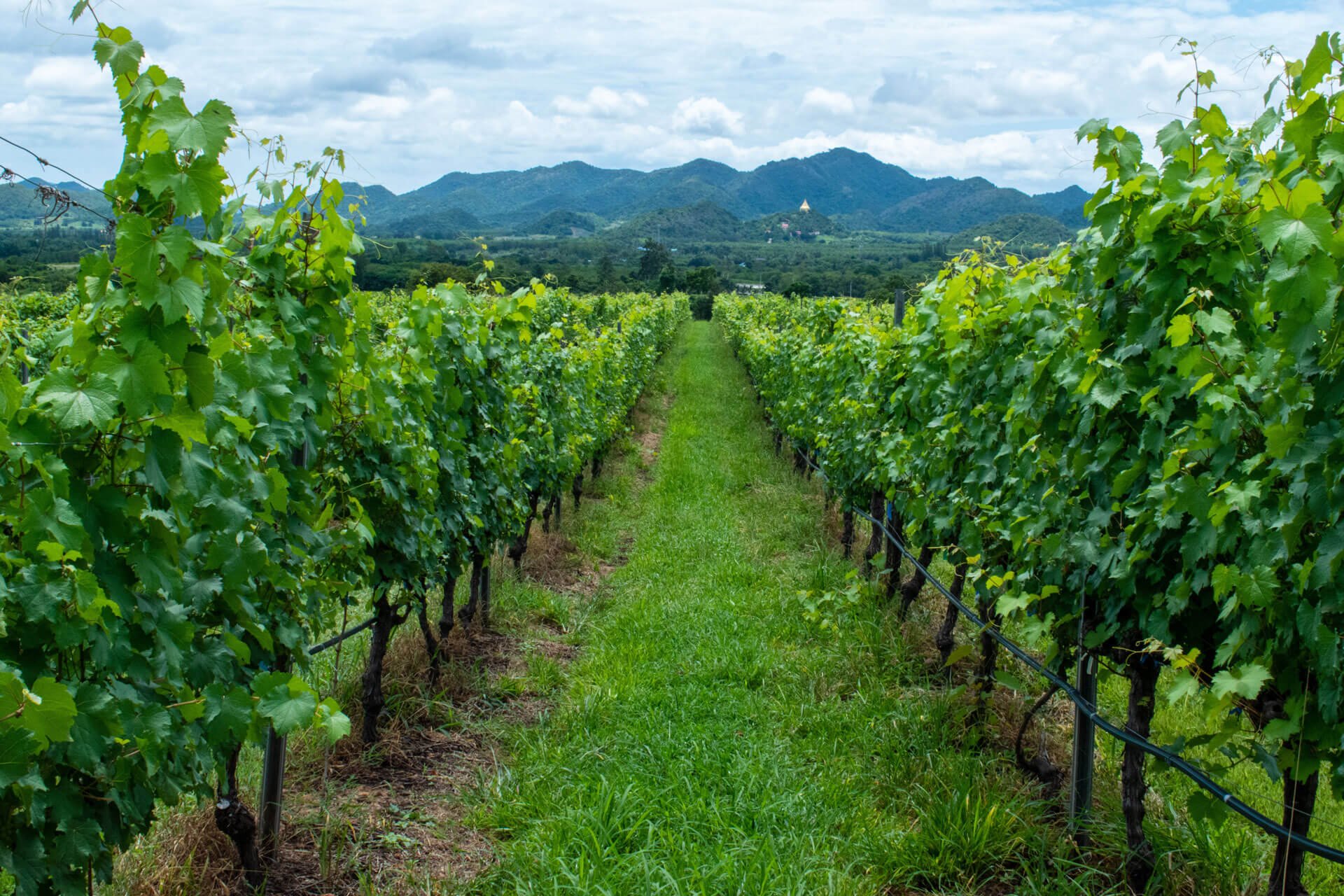
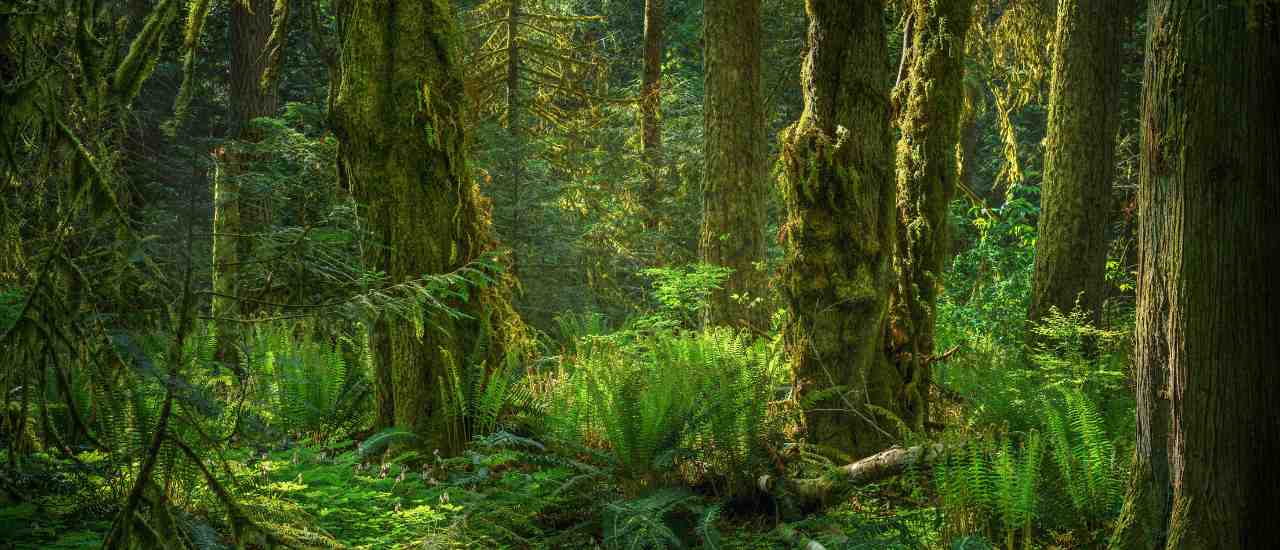
21st March signifies more than just a date—it’s International Forest Day, a time to reflect on the pivotal role forests play in sustaining life as we know it. From nurturing biodiversity to safeguarding human health, forests are our most reliable allies. As we commemorate this day, let’s delve into the myriad benefits forests offer and explore actionable steps to protect and preserve these precious ecosystems for generations to come.
The Importance Of Forests For Biodiversity
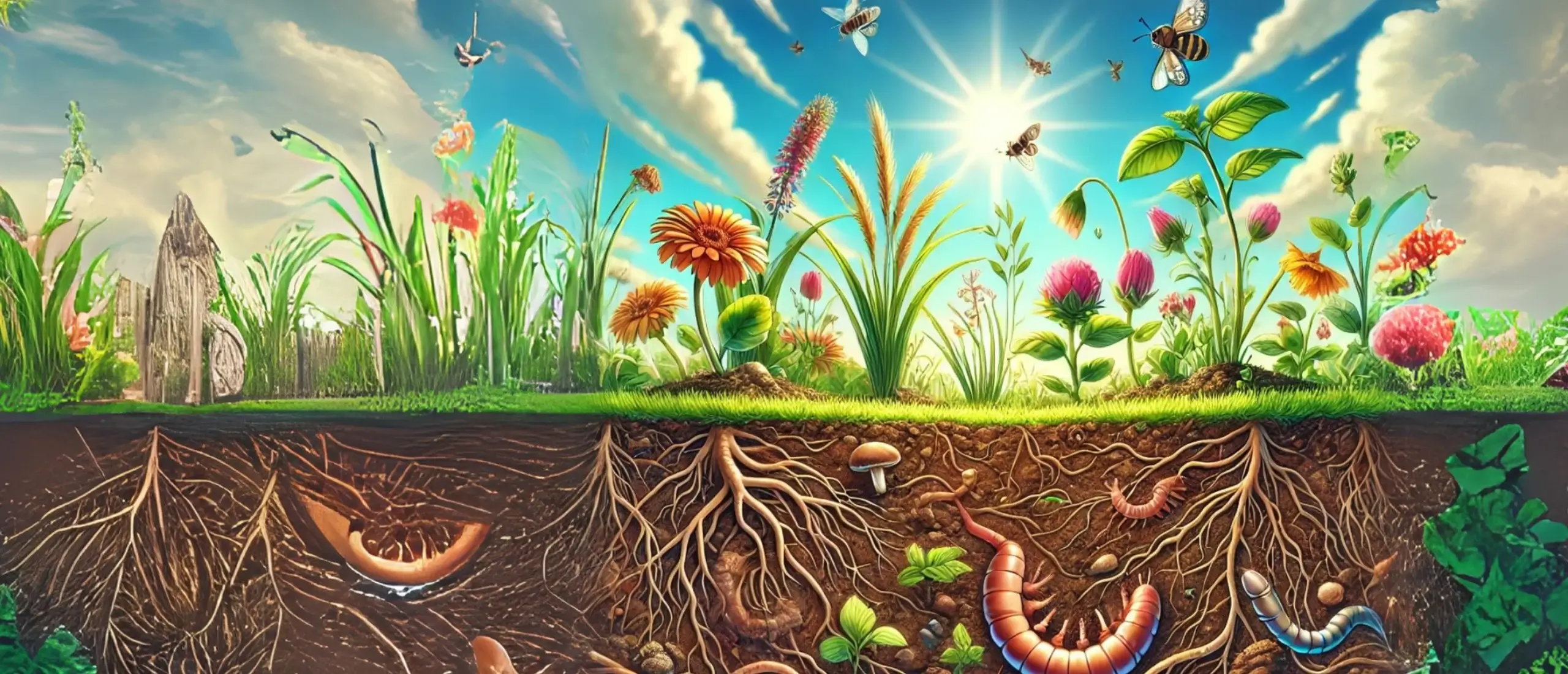
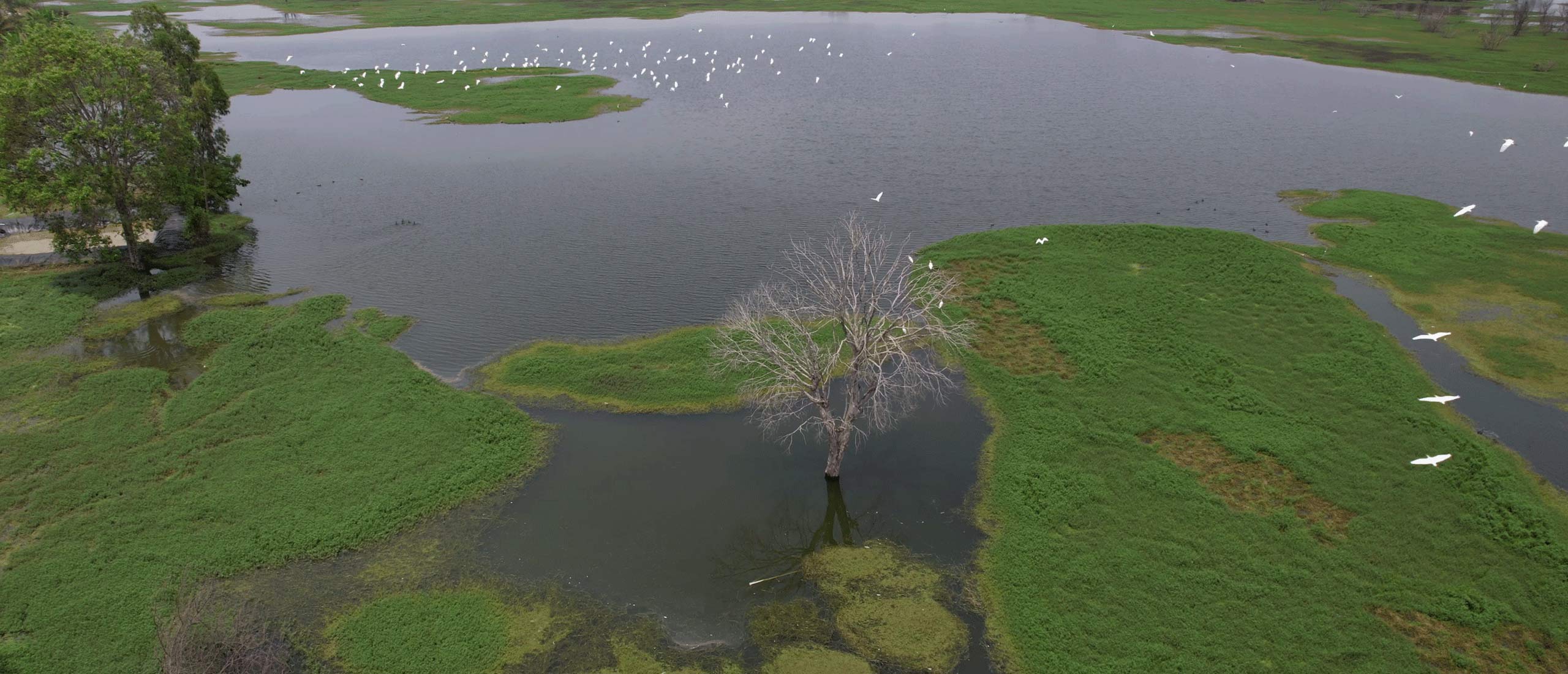
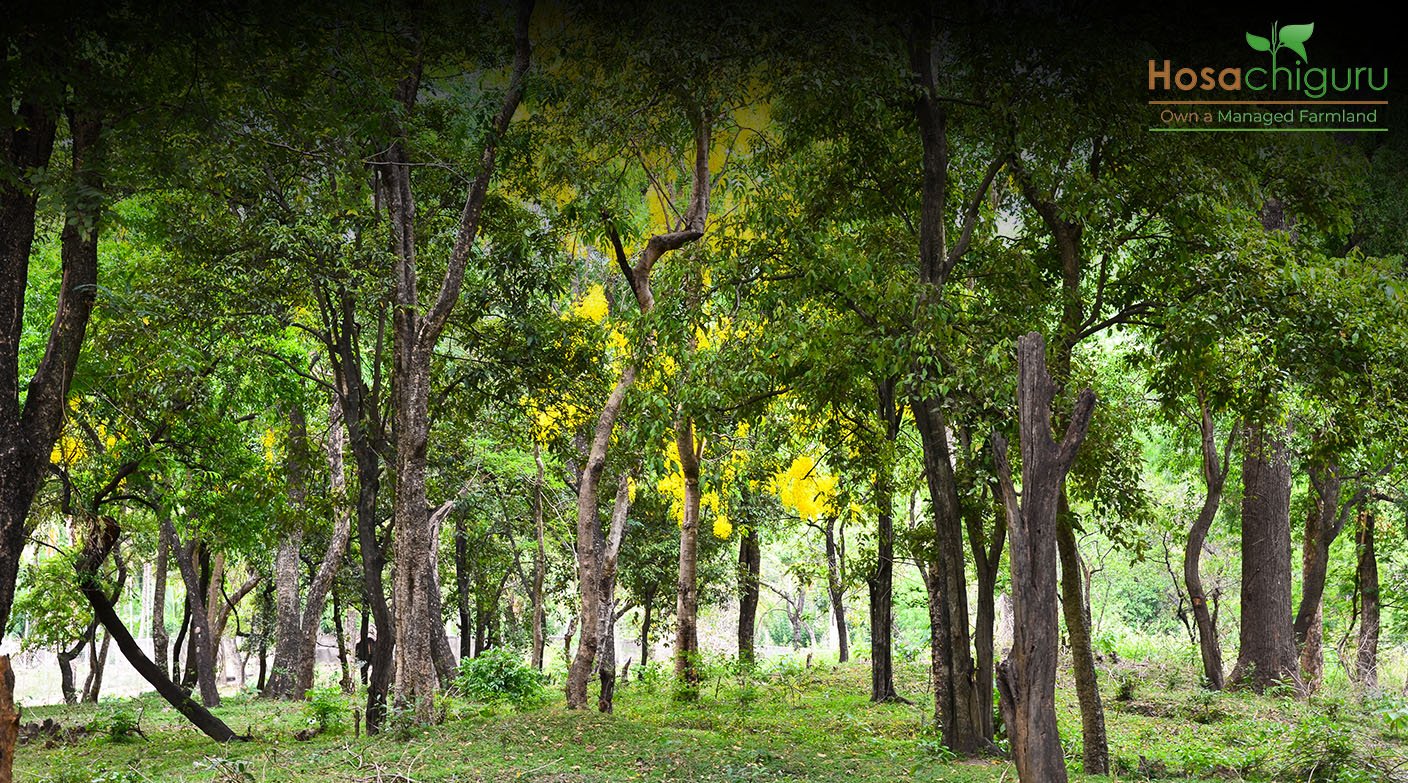
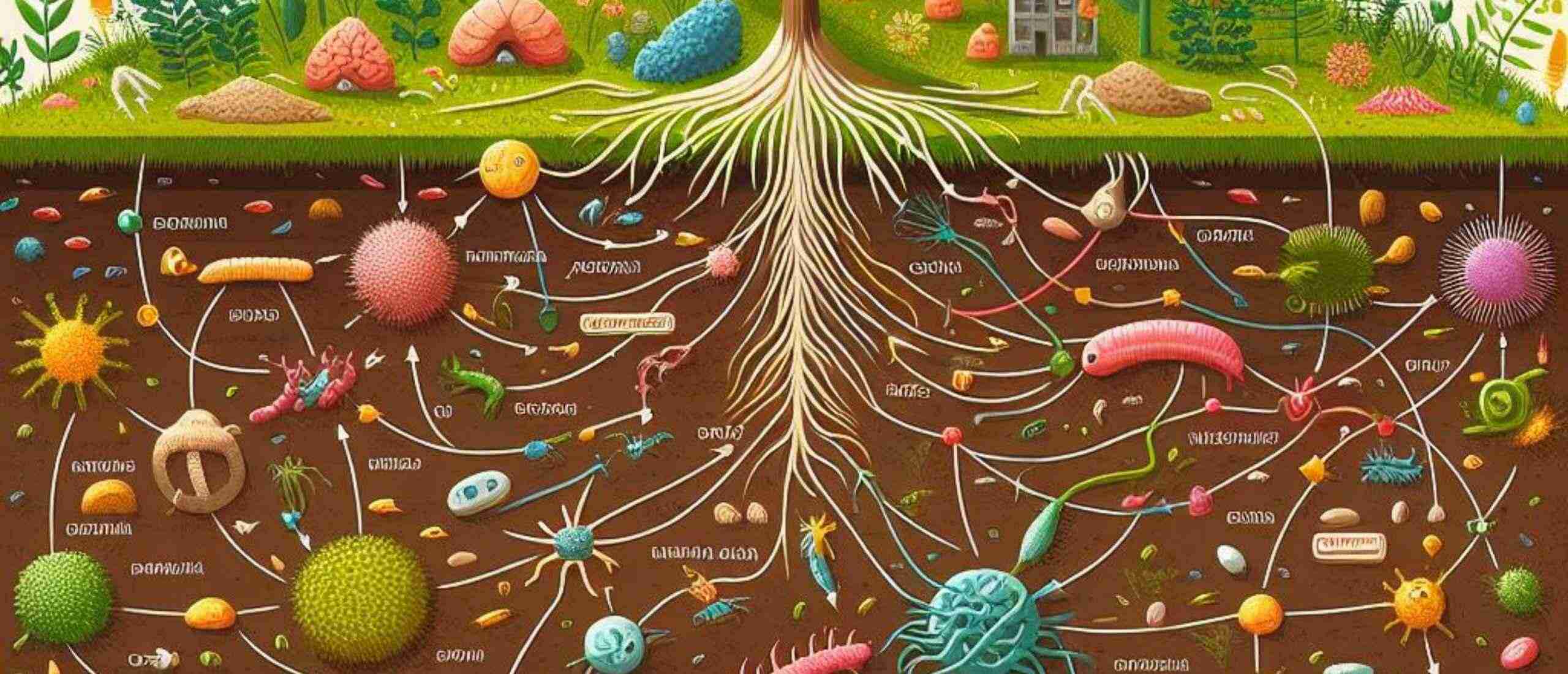
Forests are bustling hubs of life, offering homes to a rich tapestry of plants, animals, and tiny organisms. With their intricate layers – from the towering canopy to the bustling understory and the teeming forest floor – they cater to the diverse needs of countless species.
These green giants play a pivotal role in maintaining a harmonious balance of life. They don’t just stand idly by; forests actively work to sustain agriculture, ensuring long-term productivity, and nurturing healthy ecosystems. They’re not just patches of trees; they’re vital ecosystems, crucial for our planet’s well-being.
Forests play a crucial role in sustaining healthy ecosystems in following ways:
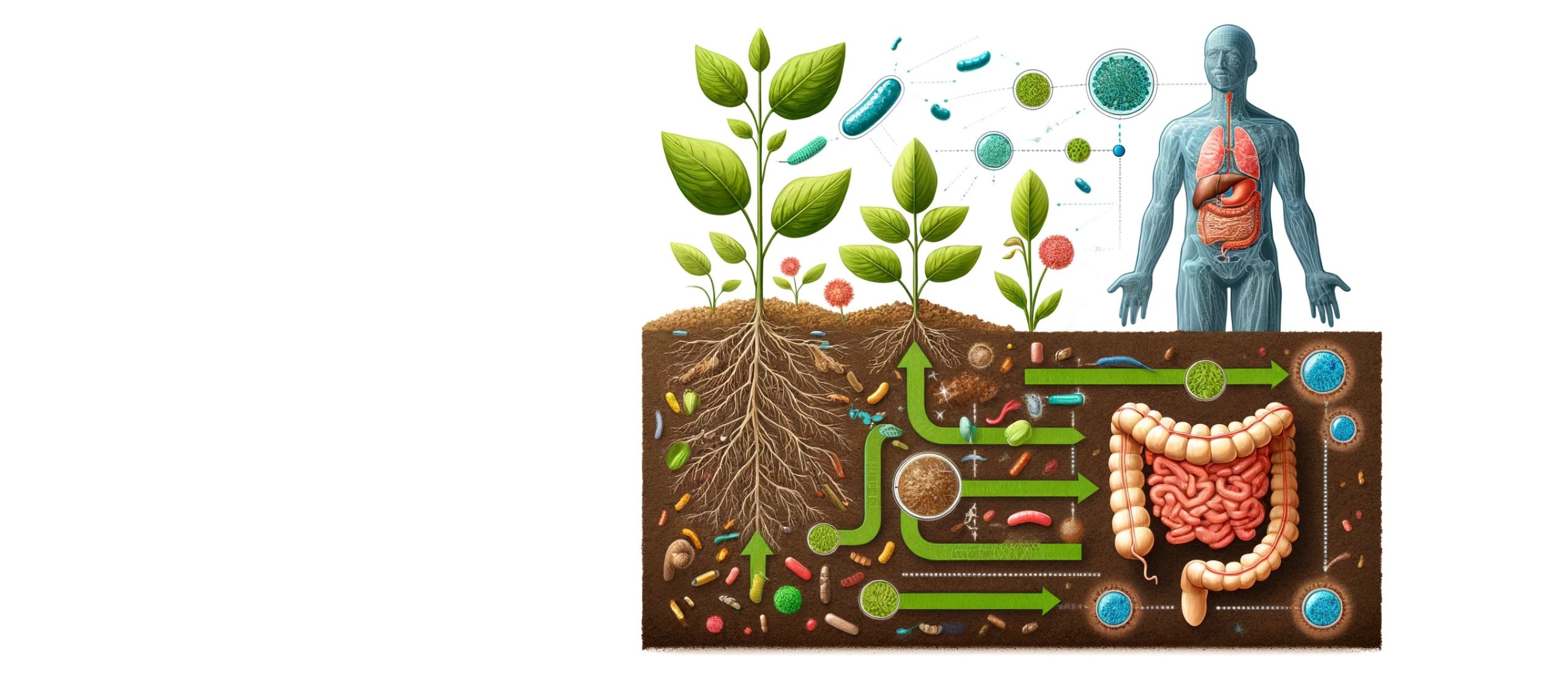
- Nutrient Cycling: Beneath the soil’s surface, a bustling ecosystem of microorganisms tirelessly recycles vital nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, crucial for plant growth. These tiny organisms decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients into the soil and facilitating processes such as nitrogen fixation. As plants absorb these nutrients through their roots, they stimulate microbial activity, further enriching the soil and the cycle of life below ground.
- Erosion Control: The dense vegetation comprising trees, shrubs, and ground cover plants serves as a formidable defense, intercepting rainfall and lessening the impact of raindrops on the soil surface. Furthermore, the accumulation of fallen leaves, branches, and organic debris creates a protective mulch layer on the forest floor, slowing down surface runoff and encouraging water infiltration, thus safeguarding against erosion. Forests act as nature’s shield, preserving the integrity of soil.
- Organic Matter Decomposition: The breakdown of organic matter is a vital process that enriches soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with micronutrients crucial for plant health. This decomposition not only nourishes the soil but also enhances its structure by fostering aggregation, boosting pore space, and improving water retention and aeration. Moreover, as organic matter breaks down, it fuels microbial activity in the soil, driving nutrient cycling, soil respiration, and the formation of stable organic matter, essential for sustaining healthy ecosystems.
- Regulating Climatic Changes: Forests play a vital role in mitigating climate change by acting as carbon sinks. Through photosynthesis, trees and plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, storing it in their biomass and in the soil organic matter. As trees grow, they continue to capture and store carbon in their wood, leaves, and roots for years to come. Moreover, land management practices like agroforestry, no-till farming, mulching, and the addition of organic matter can enhance soil carbon sequestration, further reducing atmospheric carbon levels. By sequestering carbon and enhancing soil health, forests contribute significantly to regulating climatic changes, safeguarding the planet for future generations.
Forests And Human Health
Life means vitality and we humans get this vitality from nature, as we are made up of elements of nature – The Panchbhutas (earth, water, air, fire and space). Thus, nature holds the power to cultivate happiness within us.
Our profound connection to nature can be described by the term biophilia, reflecting a deep-seated affinity for the natural world. The serene beauty of lush green landscapes, the gentle rustle of leaves, the cheerful melody of bird songs, and the earthly aroma of forests evoke positive emotions that serve to alleviate stress and induce relaxation.
In the face of modern anxiety, a prevalent plague upon mental health, we find solace in practices like “shinrin-yoku”, the Japanese concept of Forest Therapy. By immersing ourselves in nature’s embrace, surrounded by its tranquil beauty, we experience a profound shift. This communion with nature yields tangible benefits, including reduced blood pressure, lowered cortisol levels, bolstered immune function, and enhanced cardiovascular health.
Another impactful activity that harnesses the power of forests to reduce stress and promote relaxation is walking barefoot on green grass, known as “earthing” or “grounding.” Through direct contact with the earth, we absorb its negative ions, believed to have mood-lifting and stress-relieving effects. These abundant negative ions possess extra electrons that may neutralize free radicals in the body, thereby alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and various health issues, while instilling a sense of positivity and peace.
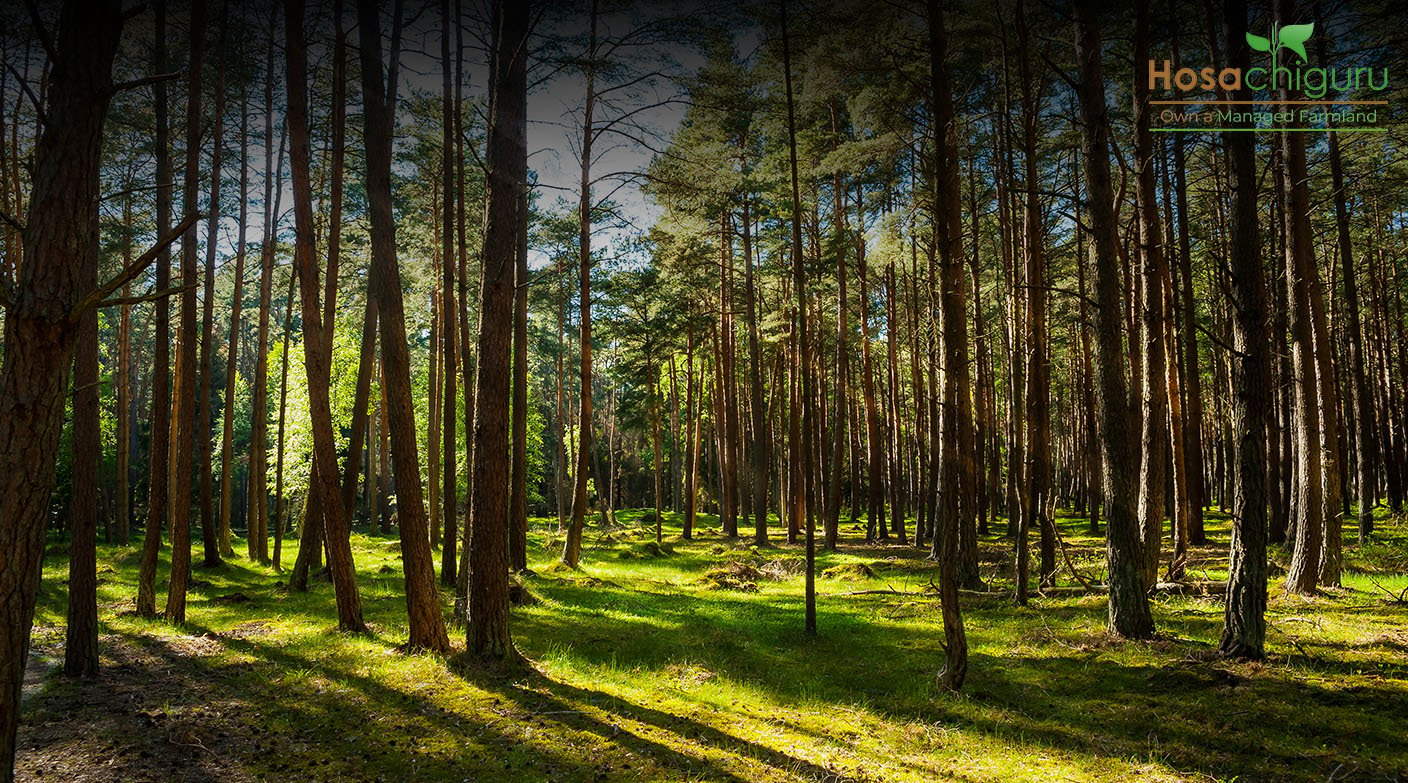
Threats To Global Forests
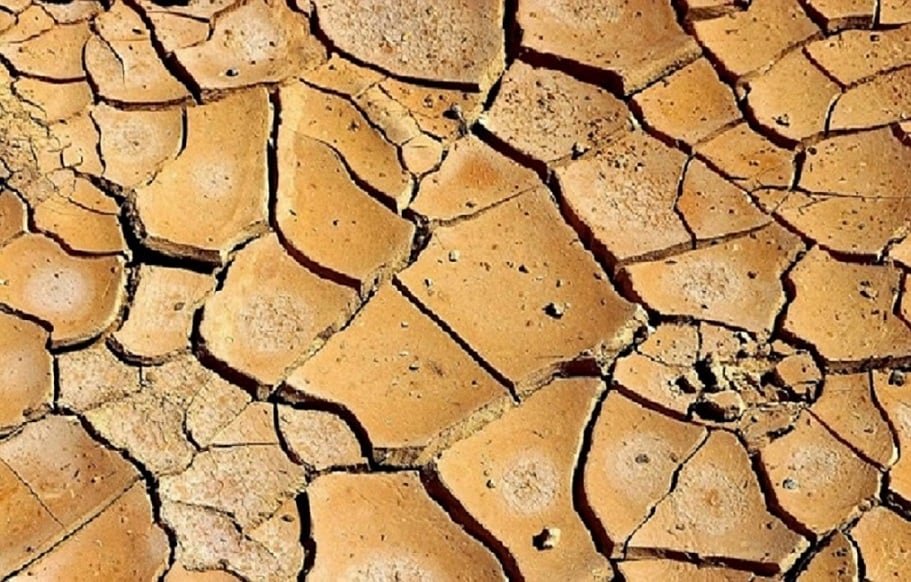
Our earth is just home to three trillion trees, almost half of what existed before human civilization. As cities grow, they take away green spaces, which affects the weather and makes extreme events like storms appear more often. This threatens the forests and makes problems like wildfires and droughts even worse.
Nature plays a vital role in supporting human life by providing shelter and safeguarding us. Moreover, biodiversity ensures a rich food source derived from the microorganisms that enrich the soil, sustaining our dietary needs. Additionally, many medicinal discoveries stem from plants and fungi. However, our detrimental actions, particularly the use of harmful chemical fertilizers, pose a significant threat to this biodiversity, impacting both land and sea ecosystems.
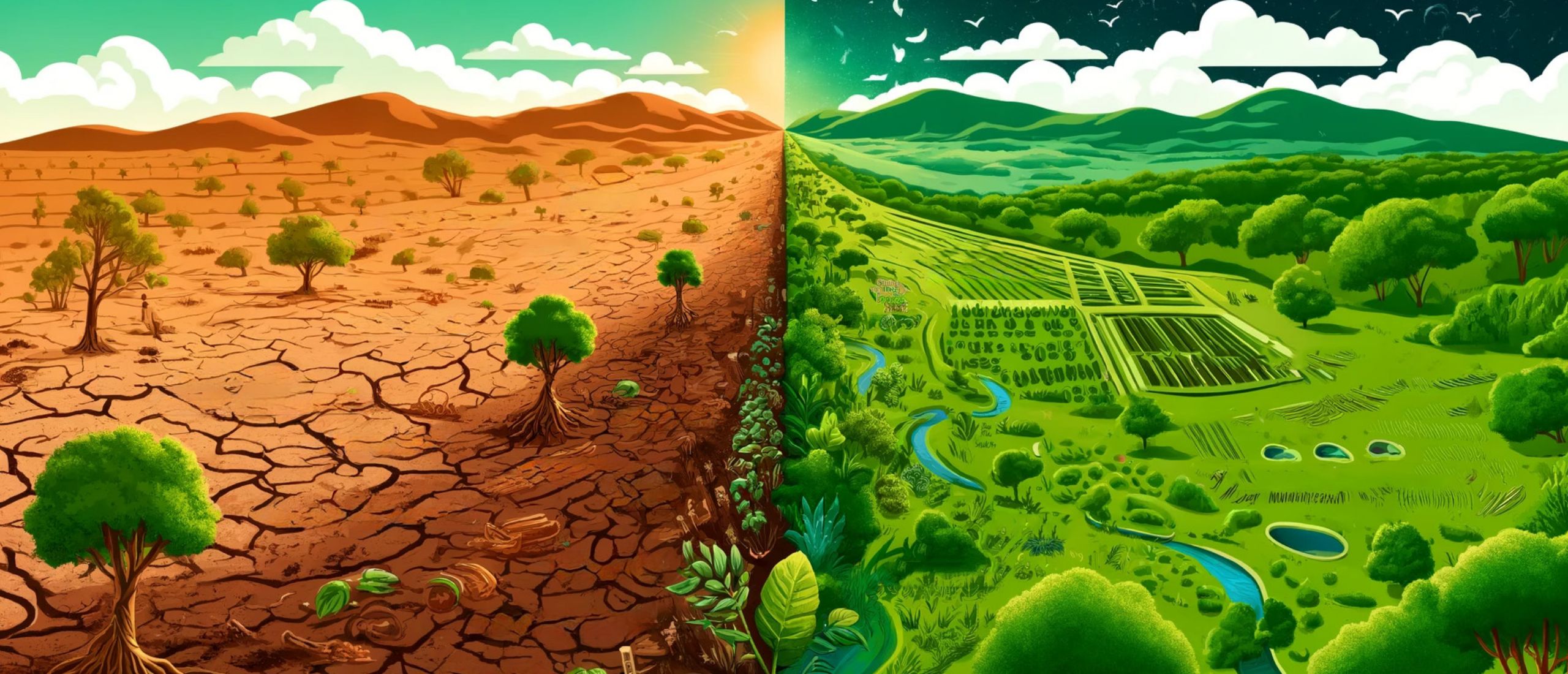
Many people believe that restoration is the key to addressing ecosystem issues and often resort to practices like monoculture, planting large quantities of the same type of tree. However, it’s crucial to recognize that restoration efforts are effective only when executed correctly.
Monoculture, characterized by one dominant species, undermines the essential biodiversity needed for a thriving planet. Continuously growing the same crop in one area can lead to imbalanced nutrients and depleted soil, as specific nutrients are used up while others remain unused. This can result in soil erosion, compaction, and reduced fertility over time.
Additionally, monoculture systems have lower capacity for carbon storage, decreased ability to retain and filter water, and diminished support for pollinators and beneficial soil microorganisms. The loss of these ecosystem services can have profound consequences for both human well-being and ecosystem health.
Innovative Forest Restoration Techniques
Nature possesses an innate capacity to flourish autonomously when provided with the right foundation. Let’s explore the strategies we can integrate to foster a thriving and sustainable green environment.
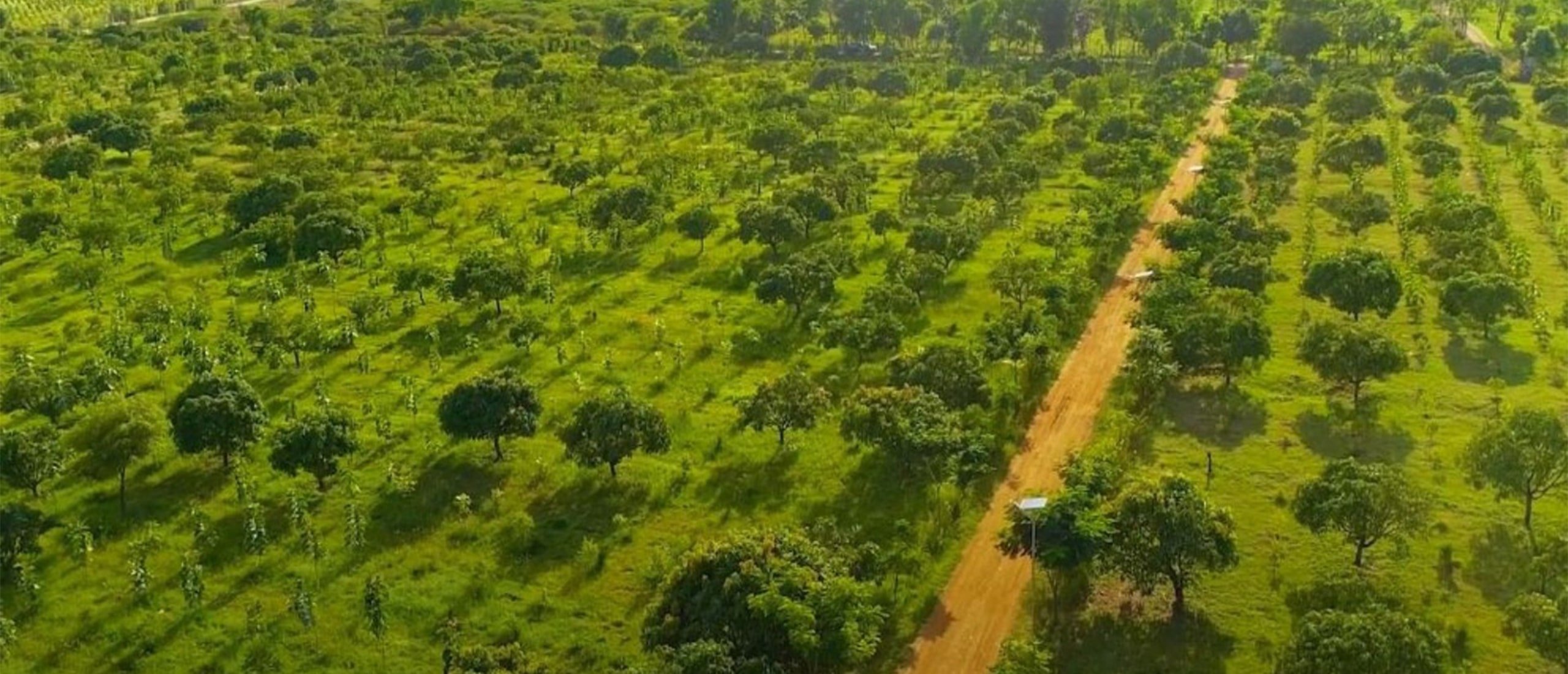
- Agroforestry: This technique involves the integration of trees or woody shrubs alongside agricultural crops and/or livestock. It enhances biodiversity by creating habitats for a diverse array of plant and animal species. Additionally, it fosters the accumulation of organic matter in the soil, thereby improving its structure, fertility, and ability to retain water.
- Regenerative Practices: Regenerative agriculture aims to emulate natural ecological principles to revitalize degraded landscapes and establish resilient, productive agricultural systems. This approach prioritizes the enhancement of soil health through various methods such as no-till farming, mulching, planting biomass crops, utilizing biochar, harvesting rainwater, and incorporating organic solutions.
- Community-Based Initiatives: These initiatives involve the collective efforts of individuals committed to conserving natural ecosystems and promoting sustainable living practices. With their expertise, these communities work towards restructuring detrimental human activities that contribute to pollution, ultimately fostering a healthier planet.
The Future Of Forests
The 2024 International Day of Forests theme, ‘Forests and Innovation’, prompts reflection on the innovative approaches needed to protect our forests. Yet, in safeguarding forests, sometimes the most effective solutions lie in ancestral wisdom, using natural elements from plants and animals while avoiding synthetic interventions.
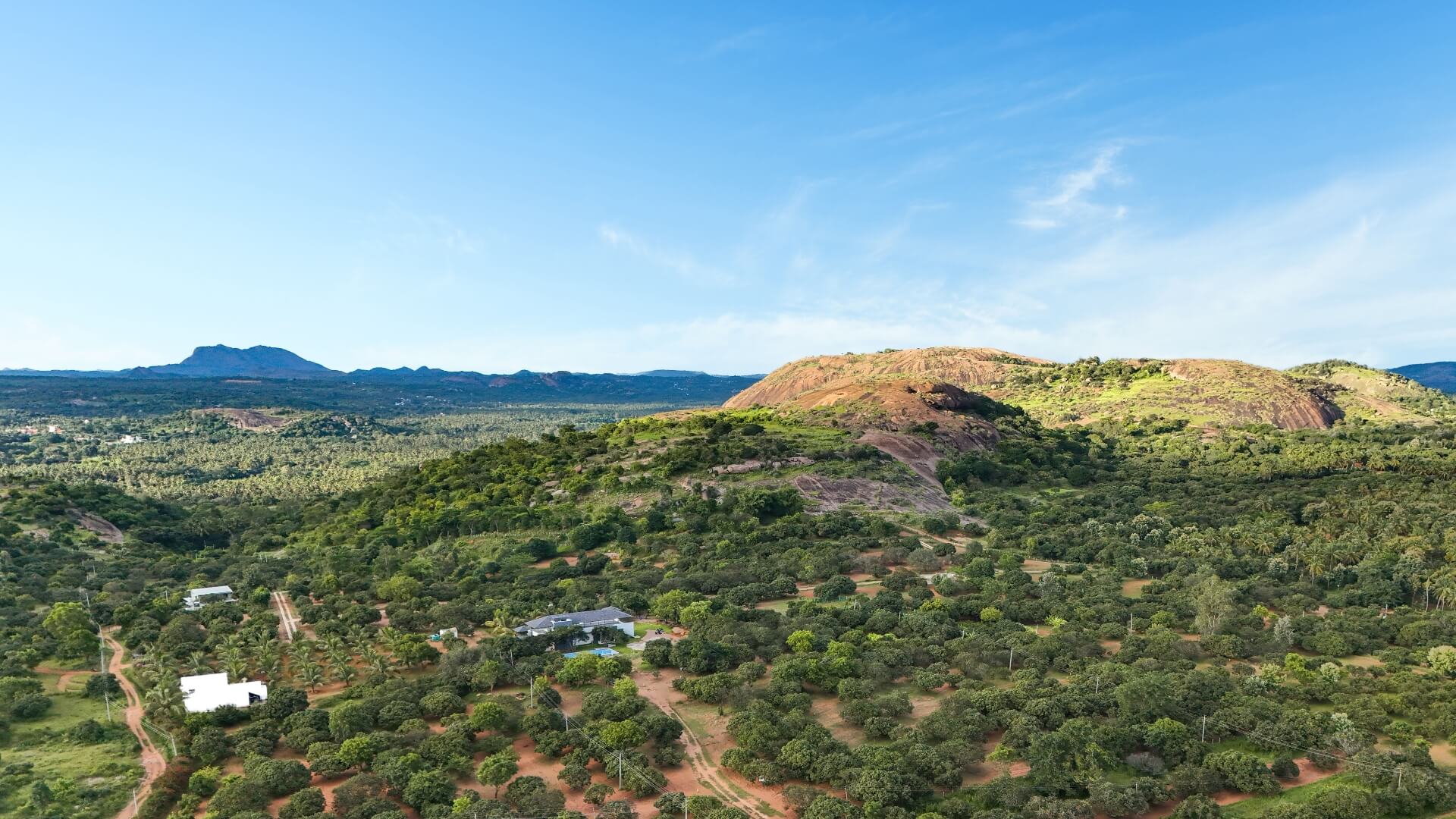
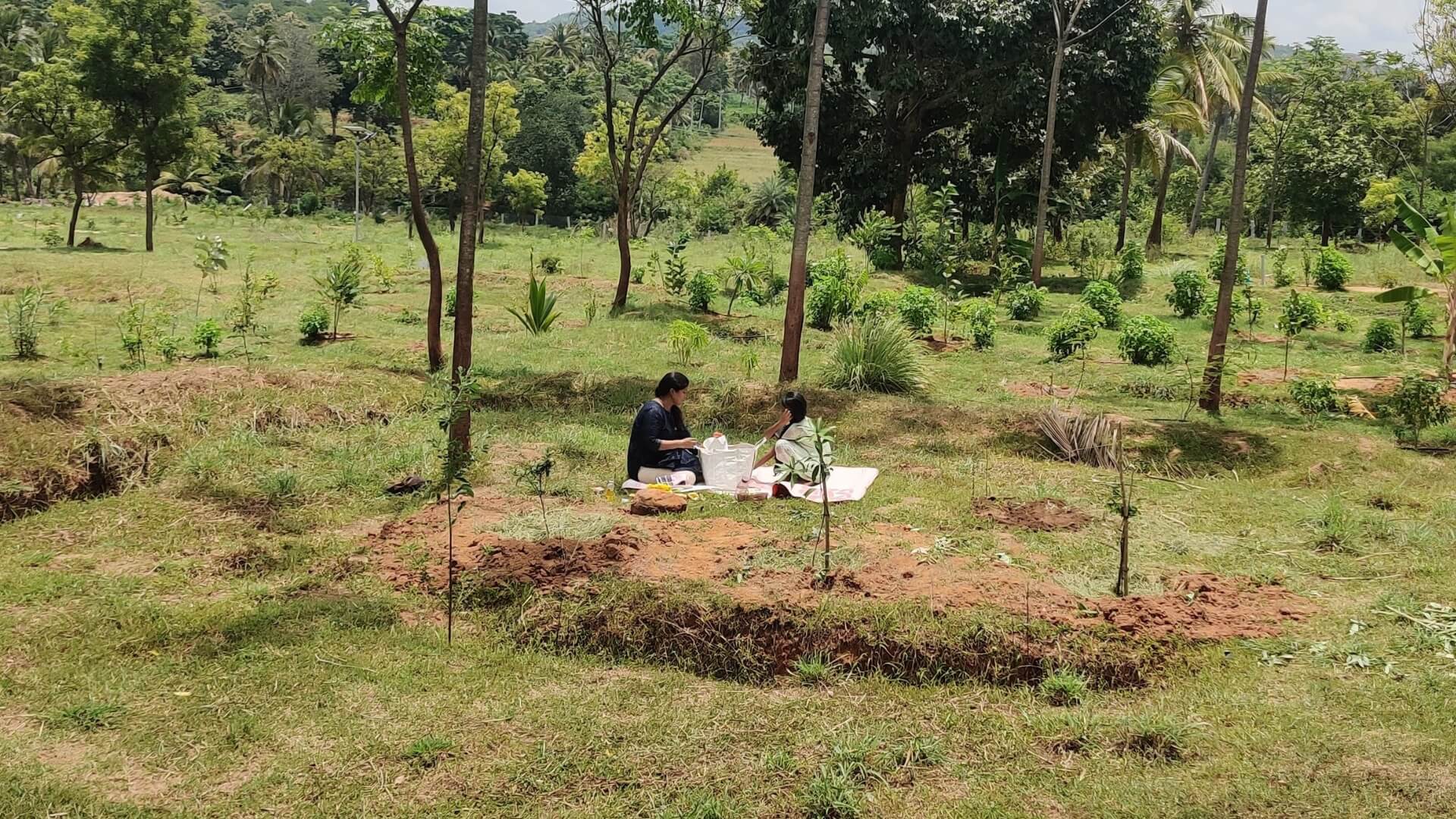
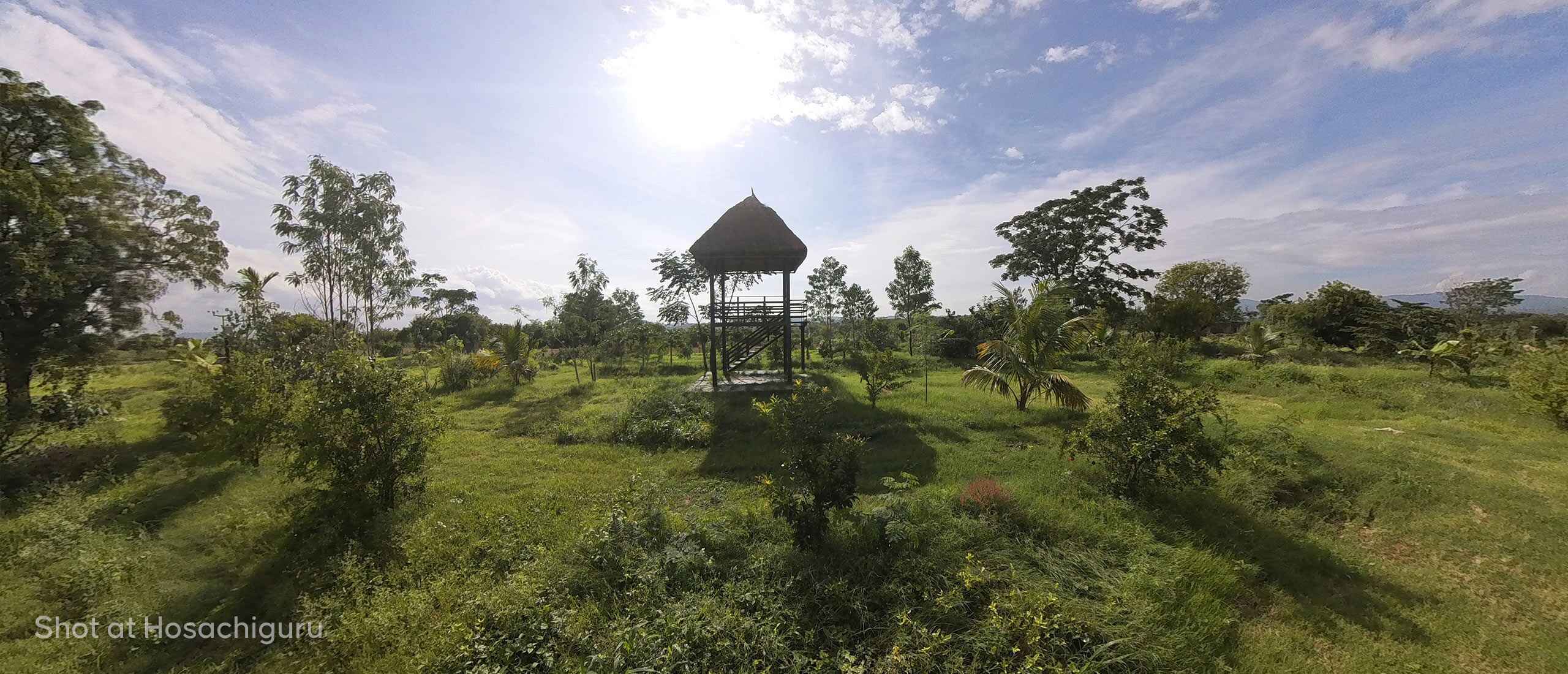
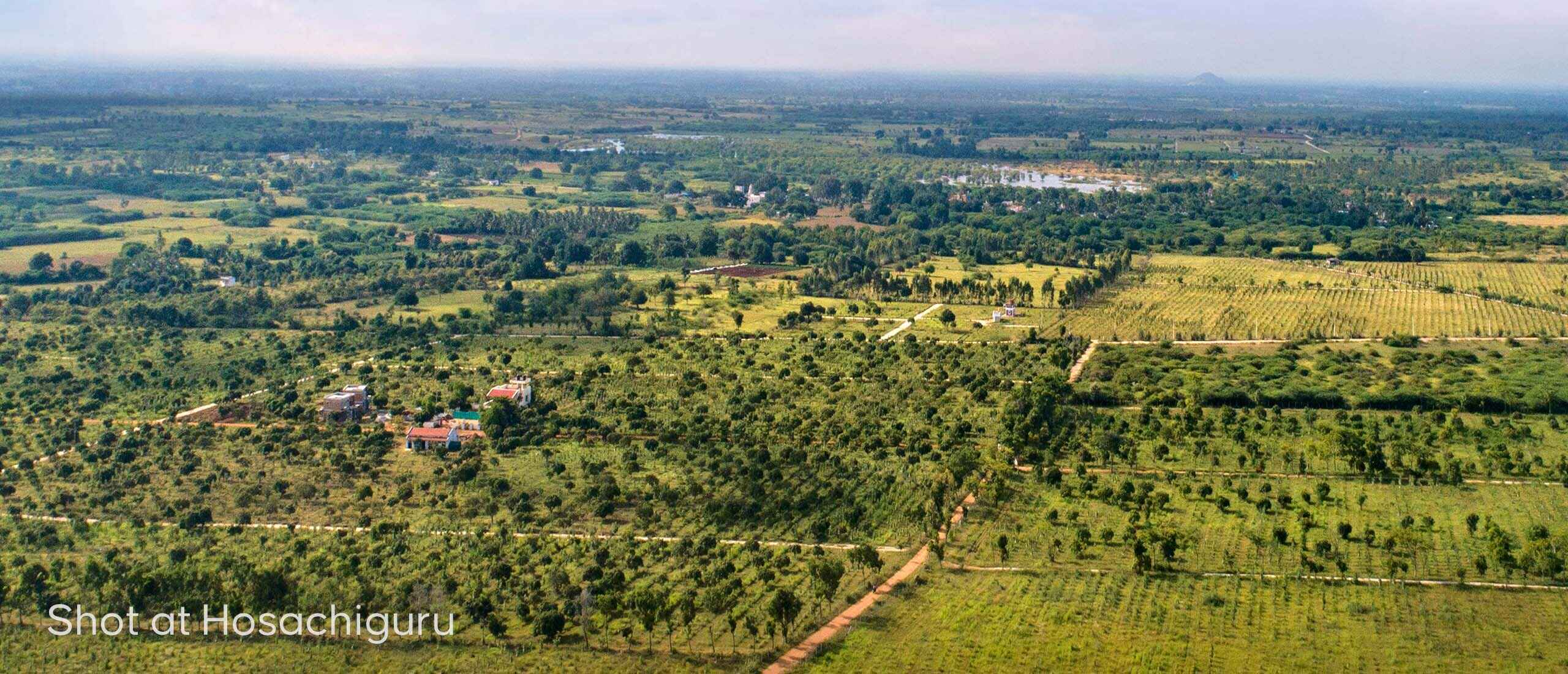
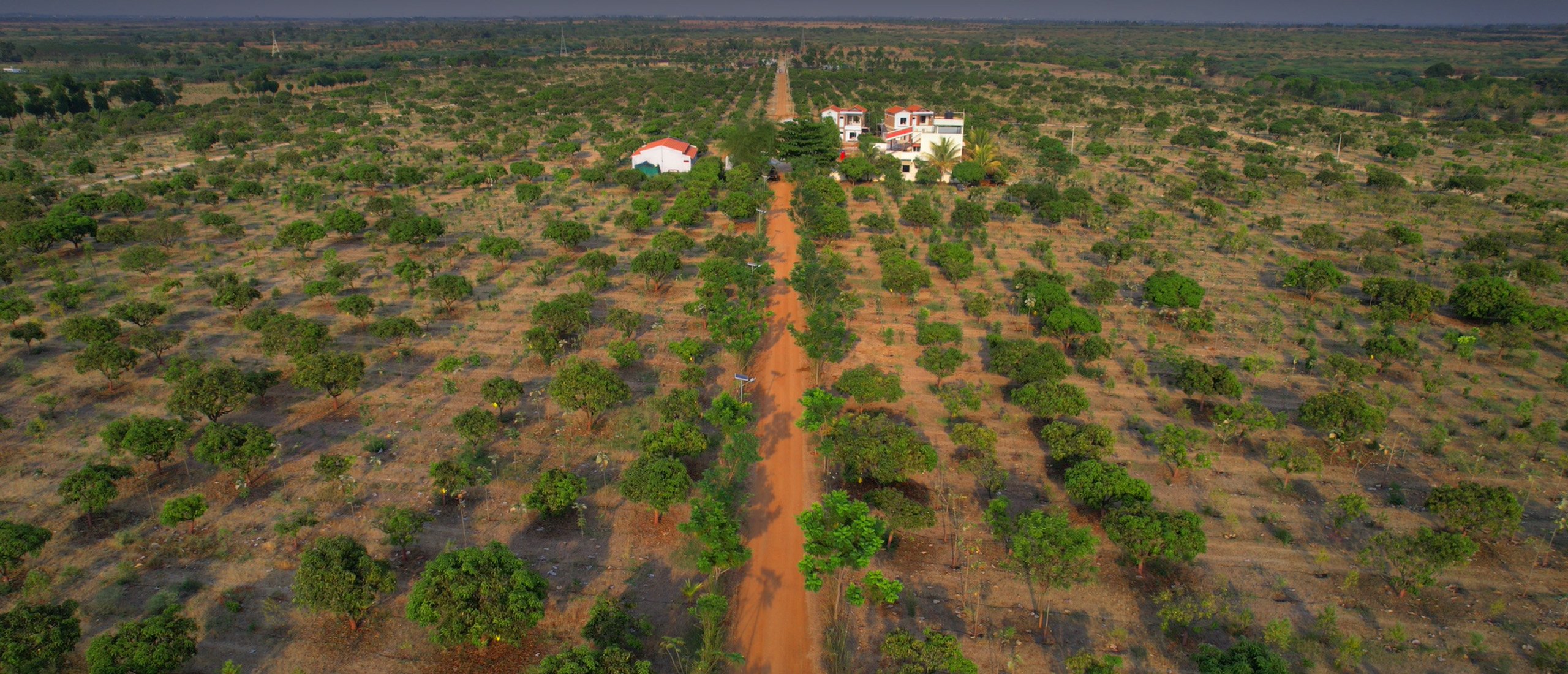
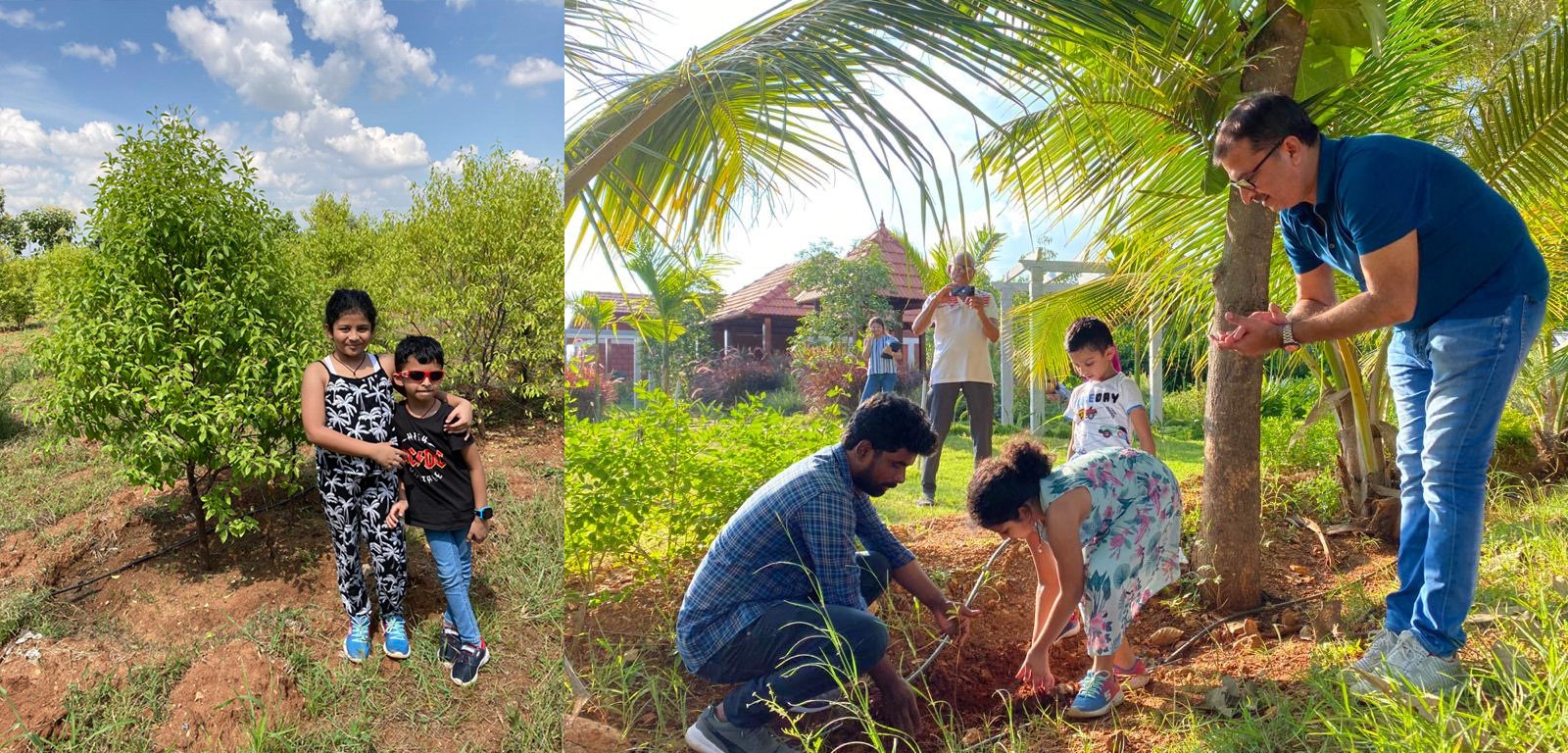
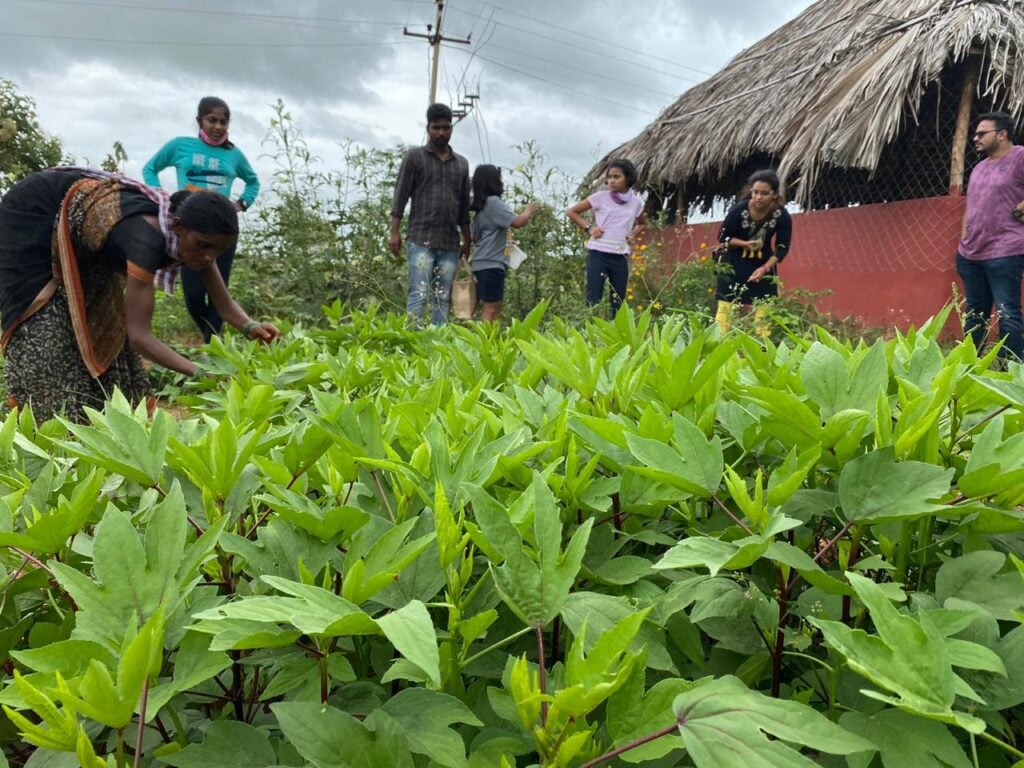
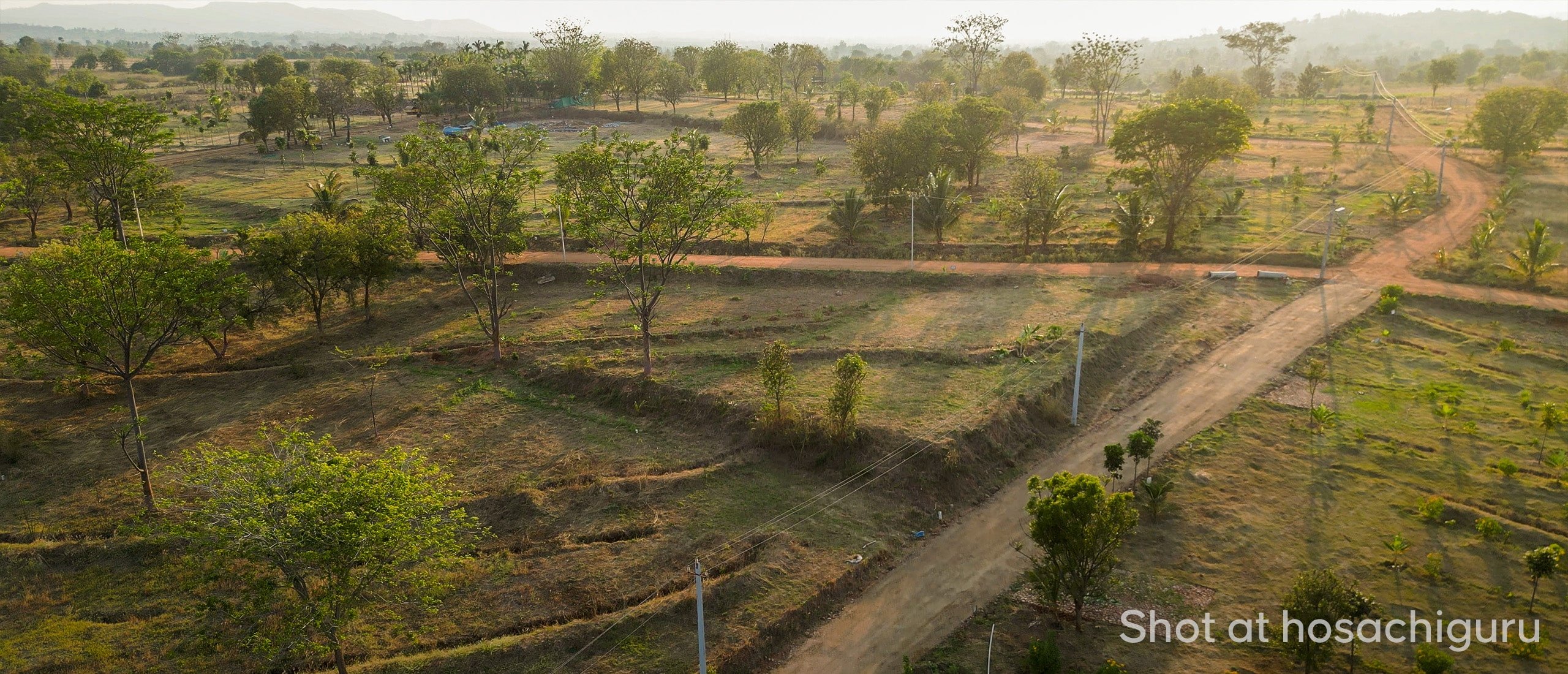
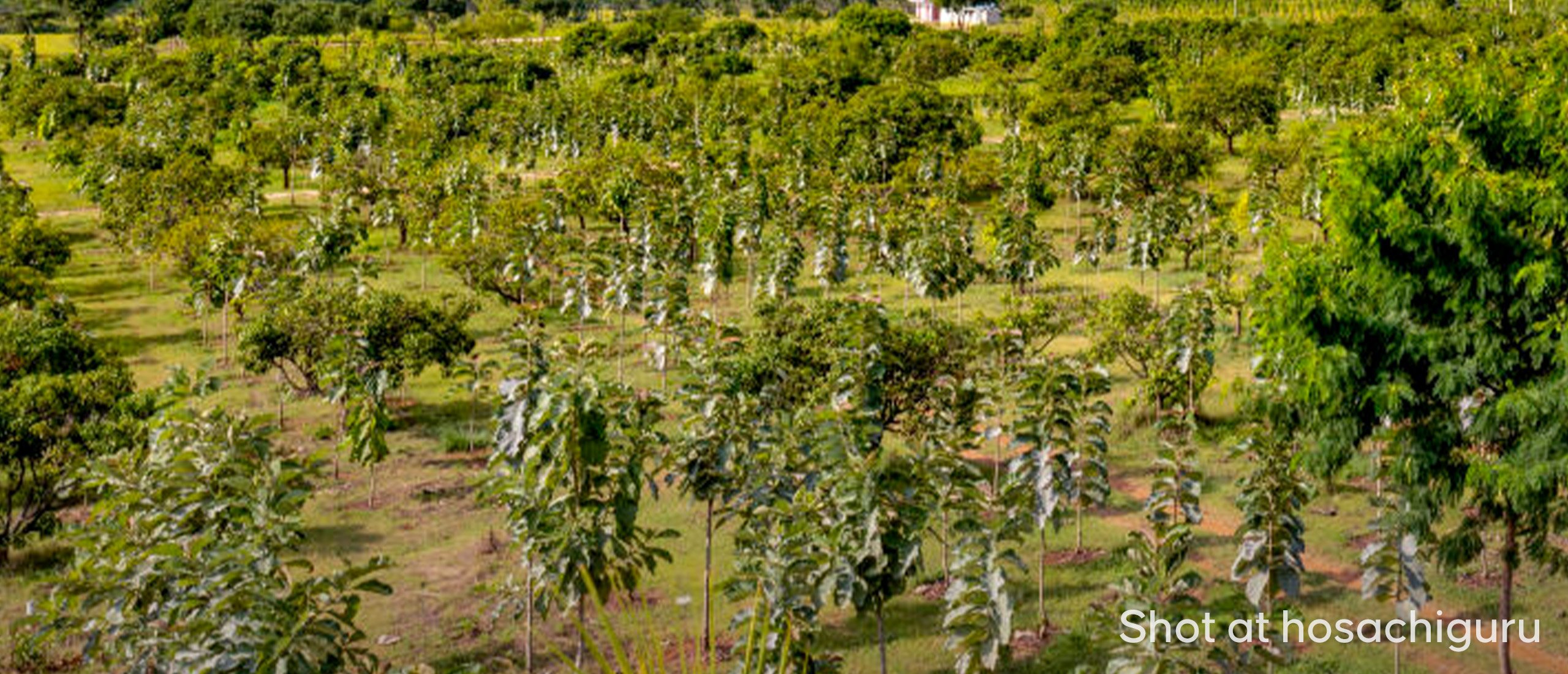
At Hosachiguru, we’re dedicated to preserving natural habitats by cultivating diverse tree species that mirror natural ecosystems. Through regenerative practices, we minimize external impacts, allowing nature to thrive independently. Supported by our passionate eco-community, we and our co-farmers today have grown over a million trees in our managed farmlands, and we strive to cultivate green spaces that nurture both our planet and our souls.
This International Day of Forests join the movement for positive change and invest in agricultural lands, plant trees, and become part of the solution. Let’s cultivate a greener future together.