March 28, 2025
As the world races to combat climate change, every activity we undertake—from air travel to the simplest act of using a mobile phone—contributes to carbon emissions. While achieving a zero-emission reality remains a distant goal, carbon credits offer a pragmatic and promising solution. These tradable permits allow companies to offset their unavoidable emissions by investing in projects that either prevent carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere or actively remove it. For every tonne of carbon dioxide offset, one carbon credit is issued, creating a robust mechanism for funding sustainable initiatives.
Governments, corporations, and organizations worldwide are increasingly leveraging carbon credits to drive investments into green projects, including forest conservation and sustainable agriculture. In this landscape, managed farmlands have emerged as a powerful yet underutilized asset in the fight against climate change.
The Carbon Market: A Growing Opportunity
The global voluntary carbon market is projected to soar to $50 billion by 2030, according to the World Bank. While forests, which cover nearly 31% of the Earth’s land, have traditionally dominated the carbon credit conversation, agricultural land—accounting for about 38% of global land use—presents an untapped potential. Through sustainable farming practices, agricultural lands can transform into carbon sinks, capturing atmospheric carbon while revitalizing ecosystems.
India, where agriculture forms the backbone of the economy, is uniquely poised to lead this transformation. The government is championing sustainable farming practices to address challenges such as overreliance on chemical inputs and the unsustainable use of natural resources. These initiatives not only align with the nation’s climate goals but also offer a new revenue stream for farmers willing to embrace change.
Carbon Credits and Global Climate Goals
Carbon credits are critical to achieving the Paris Agreement’s objective of limiting global warming to below 2°C, with an aspirational target of 1.5°C. Article 6 of the agreement provides a framework for international carbon markets, enabling countries and corporations to trade emissions reductions. By investing in carbon credits, businesses and nations contribute to global climate goals while offsetting their carbon footprint—a win-win scenario for the planet and the economy.
Transforming Agriculture with Sustainable Practices
Sustainable agricultural practices such as regenerative farming, agroecology, and climate-resilient agriculture offer multi-faceted benefits:
Environmental Gains: Improved soil microbial health, enhanced water resource availability, increased biodiversity, and ecosystem restoration.
Economic Benefits: Reduced dependence on costly chemical inputs, increased yields, and access to premium markets for sustainably produced food.
Healthier soils, enriched with organic carbon, yield healthier crops while reducing post-harvest losses. Crop diversification, a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, not only ensures food security but also mitigates risks from pests and diseases.
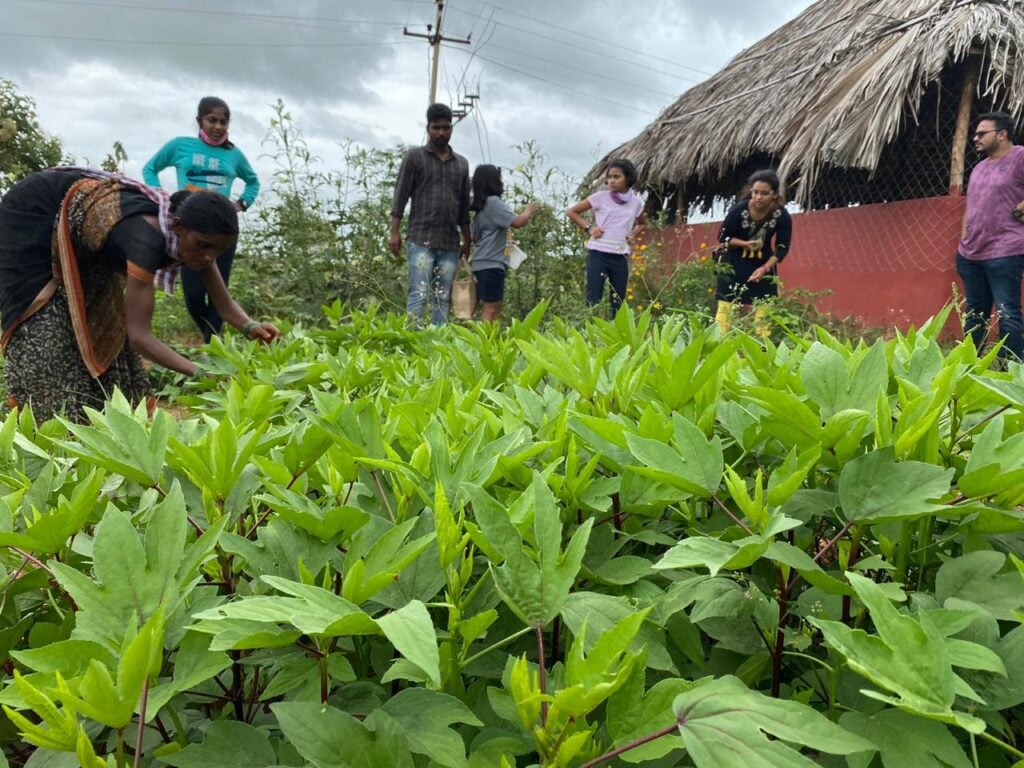
Case Study: Karnataka’s Afforestation Success
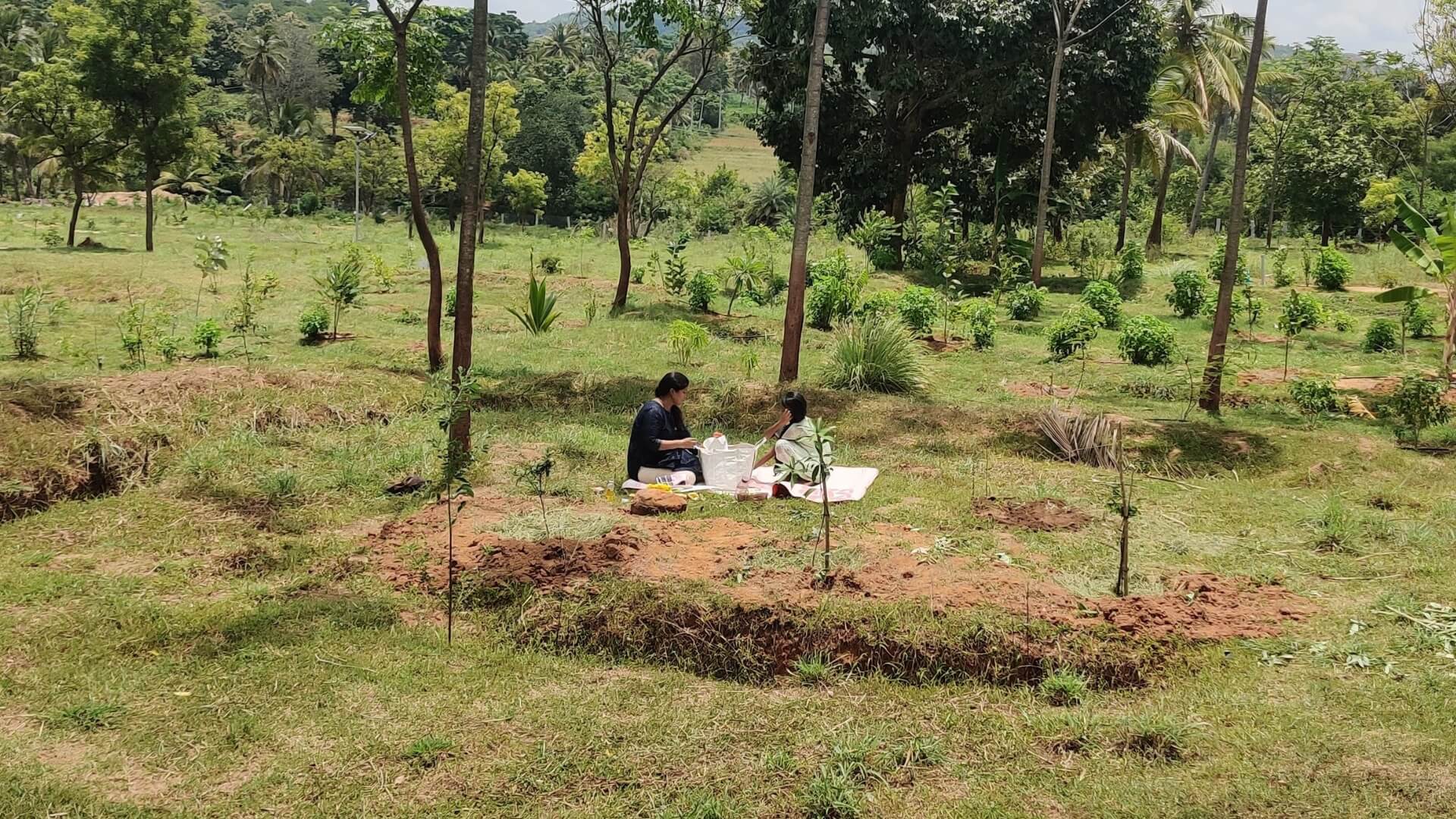
The transformative potential of sustainable farming is exemplified by a 10-year afforestation project in Bagepalli, Karnataka. Local farmers planted fruit and fodder trees—mango, cashew, and tamarind—on degraded lands. Despite early challenges, including low sapling survival due to erratic weather, the adoption of climate-resilient techniques improved survival rates by 40%.
The project, certified under the Gold Standard for the Global Goals, sequestered substantial greenhouse gases, earning 91,092 carbon credits. This translated into significant financial gains: ₹26.18 crore in 2019 and ₹4.4 crore in 2021. These funds empowered local families, revitalized degraded lands, and advanced global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focused on responsible resource use, climate action, and ecosystem restoration.
The Green Credit Programme: Amplifying Impact
India’s Green Credit Programme (GCP), an initiative aligned with Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), complements carbon credits by incentivizing green activities such as tree plantation, water management, sustainable agriculture, and waste management. Projects generating green credits can simultaneously earn carbon credits, creating dual revenue streams. Managed farmlands stand to benefit immensely from this synergistic opportunity.
The Promise of Managed Farmlands
Managed farmlands hold unparalleled potential in addressing both climate change and food security challenges. By adopting sustainable practices, farmers can:
Sequester Carbon: Boost soil organic carbon and actively reduce atmospheric CO2 levels.
Enhance Productivity: Improve soil health and biodiversity for higher and more sustainable yields.
Access Premium Markets: Cater to a growing consumer base seeking sustainably produced food.
Empower Communities: Generate financial and social benefits, particularly for marginalized groups.
Conclusion: A New Frontier for Farmers
The integration of carbon credits with managed farmlands is not just an environmental imperative but also an economic opportunity waiting to be seized. By embracing sustainable farming practices, farmers can unlock significant revenue streams while mitigating climate risks.
With the voluntary carbon market set to expand exponentially in the coming years, the time is ripe for farmers, policymakers, and businesses to collaborate. The question is no longer whether managed farmlands can play a role in climate mitigation but rather: Is your land ready to cash in on this billion-dollar opportunity?